1 南京大学电子科学与工程学院,江苏 南京 210023
2 南京大学集成电路学院,江苏 苏州 215163
3 南京大学现代工程与应用科学学院,江苏 南京 210023
4 武进南京大学未来技术创新研究院,江苏 常州 213153
二维光子晶体板的介电常数分布具有面内的空间周期性,并支持可辐射到自由空间的导模共振。这些辐射到远场的模式可以用动量进行标记,并具有偏振态,因此可以定义动量空间中的偏振场。通过研究不同结构参数和对称性下偏振场的特性以及与外界相互作用的规律,能够为光场操控提供新思路。本文介绍了二维光子晶体板在动量空间中的偏振场的相关特性,并综述了近年来相关的研究和应用。
物理光学 光子晶体 偏振场 偏振奇点 拓扑电荷 光学学报
2024, 44(10): 1026003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Photonic Chips, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
2 Centre for Artificial-Intelligence Nanophotonics, School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
3 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, and College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
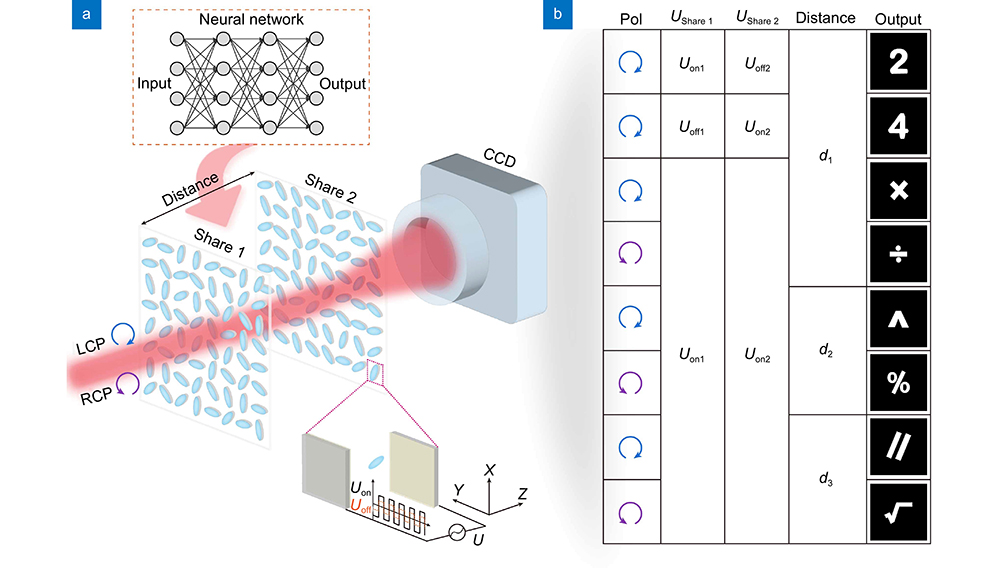
Secret sharing is a promising technology for information encryption by splitting the secret information into different shares. However, the traditional scheme suffers from information leakage in decryption process since the amount of available information channels is limited. Herein, we propose and demonstrate an optical secret sharing framework based on the multi-dimensional multiplexing liquid crystal (LC) holograms. The LC holograms are used as spatially separated shares to carry secret images. The polarization of the incident light and the distance between different shares are served as secret keys, which can significantly improve the information security and capacity. Besides, the decryption condition is also restricted by the applied external voltage due to the variant diffraction efficiency, which further increases the information security. In implementation, an artificial neural network (ANN) model is developed to carefully design the phase distribution of each LC hologram. With the advantage of high security, high capacity and simple configuration, our optical secret sharing framework has great potentials in optical encryption and dynamic holographic display.
holographic encryption optical secret sharing cascaded liquid crystal hologram multi-dimensional multiplexing Opto-Electronic Advances
2024, 7(1): 230121
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronic and Optical Engineering & College of Flexible Electronics (Future Technology), Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210023, China
2 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
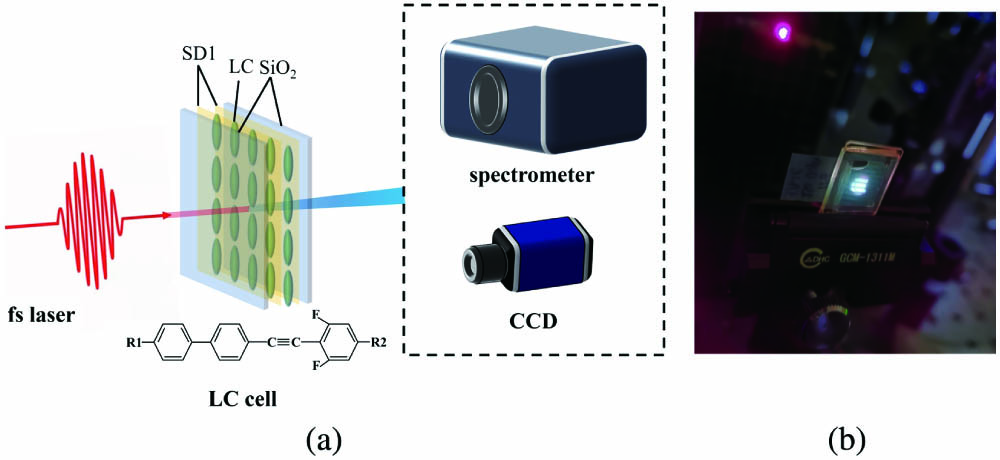
This study investigated direct fluorescence generation from a nematic liquid crystal (NLC) NJU-LDn-4 under femtosecond laser excitation. The absorption, transmittance, excitation, and emission spectra of the NLC were assessed. The relationship between the femtosecond pump power and fluorescence intensity was analyzed, revealing a quadratic increase and indicating that two-photon absorption (2PA) is the primary fluorescence mechanism. The LC microstructure was designed using photoalignment technology, allowing the generated fluorescence to reflect the corresponding structure. This research can establish a foundation for tunable LC microstructured fluorescence, with potential applications in fluorescence microscopy and optoelectronics.
liquid crystal femtosecond laser fluorescence microstructure Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 033801
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Nanjing University, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, National Laboratory of Solid-State Microstructures, Nanjing, China
2 Nanjing University, School of Electronic Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing, China
3 Nanjing University, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, Nanjing, China
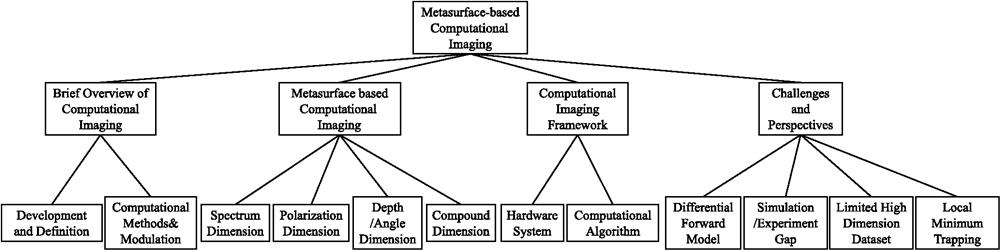
Metasurface-based imaging has attracted considerable attention owing to its compactness, multifunctionality, and subwavelength coding capability. With the integration of computational imaging techniques, researchers have actively explored the extended capabilities of metasurfaces, enabling a wide range of imaging methods. We present an overview of the recent progress in metasurface-based imaging techniques, focusing on the perspective of computational imaging. Specifically, we categorize and review existing metasurface-based imaging into three main groups, including (i) conventional metasurface design employing canonical methods, (ii) computation introduced independently in either the imaging process or postprocessing, and (iii) an end-to-end computation-optimized imaging system based upon metasurfaces. We highlight the advantages and challenges associated with each computational metasurface-based imaging technique and discuss the potential and future prospects of the computational boosted metaimager.
metasurface computational imaging inverse problem algorithm Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(1): 014002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Engineering and Applied Sciences and Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
2 School of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
3 Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210008, China
Systemic blood circulation is one of life activity’s most important physiological functions. Continuous noninvasive hemodynamic monitoring is essential for the management of cardiovascular status. However, it is difficult to achieve systemic hemodynamic monitoring with the daily use of current devices due to the lack of multichannel and time-synchronized operation capability over the whole body. Here, we utilize a soft microfiber Bragg grating group to monitor spatiotemporal hemodynamics by taking advantage of the high sensitivity, electromagnetic immunity, and great temporal synchronization between multiple remote sensor nodes. A continuous systemic hemodynamic measurement technique is developed using all-mechanical physiological signals, such as ballistocardiogram signals and pulse waves, to illustrate the actual mechanical process of blood circulation. Multiple hemodynamic parameters, such as systemic pulse transit time, heart rate, blood pressure, and peripheral resistance, are monitored using skin-like microfiber Bragg grating patches conformally attached at different body locations. Relying on the soft microfiber Bragg grating group, the spatiotemporal hemodynamic monitoring technique opens up new possibilities in clinical medical diagnosis and daily health management.
spatiotemporal hemodynamic monitor skin-like photonic devices microfiber Bragg grating Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(11): 230018
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Key Laboratory of Intelligent Optical Sensing and Manipulation, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, and College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
2 School of Instrumentation and Optoelectronic Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
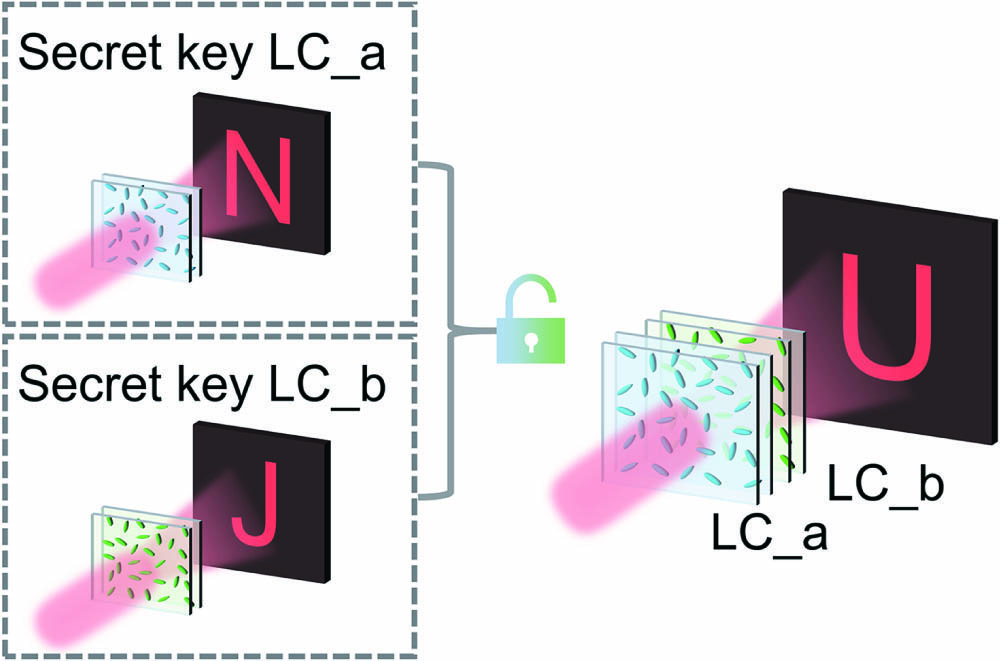
Cascaded holography coupled with the secret-sharing scheme has recently gained considerable attention due to its enhanced information processing and encryption capabilities. Here, we propose a new holographic iterative algorithm and present the implementation of cascaded liquid crystal (LC) holography for optical encryption. Each LC layer acts as the secret key and can generate a distinct holographic image. By cascading two LC elements, a new holographic image is formed. Additionally, we showcase the dynamic optical encryption achieved by electrically switching LCs with combined electric keys. This work may offer promising applications in optical cryptography, all-optical computing, and data storage.
liquid crystals holography optical encryption Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(12): 120003
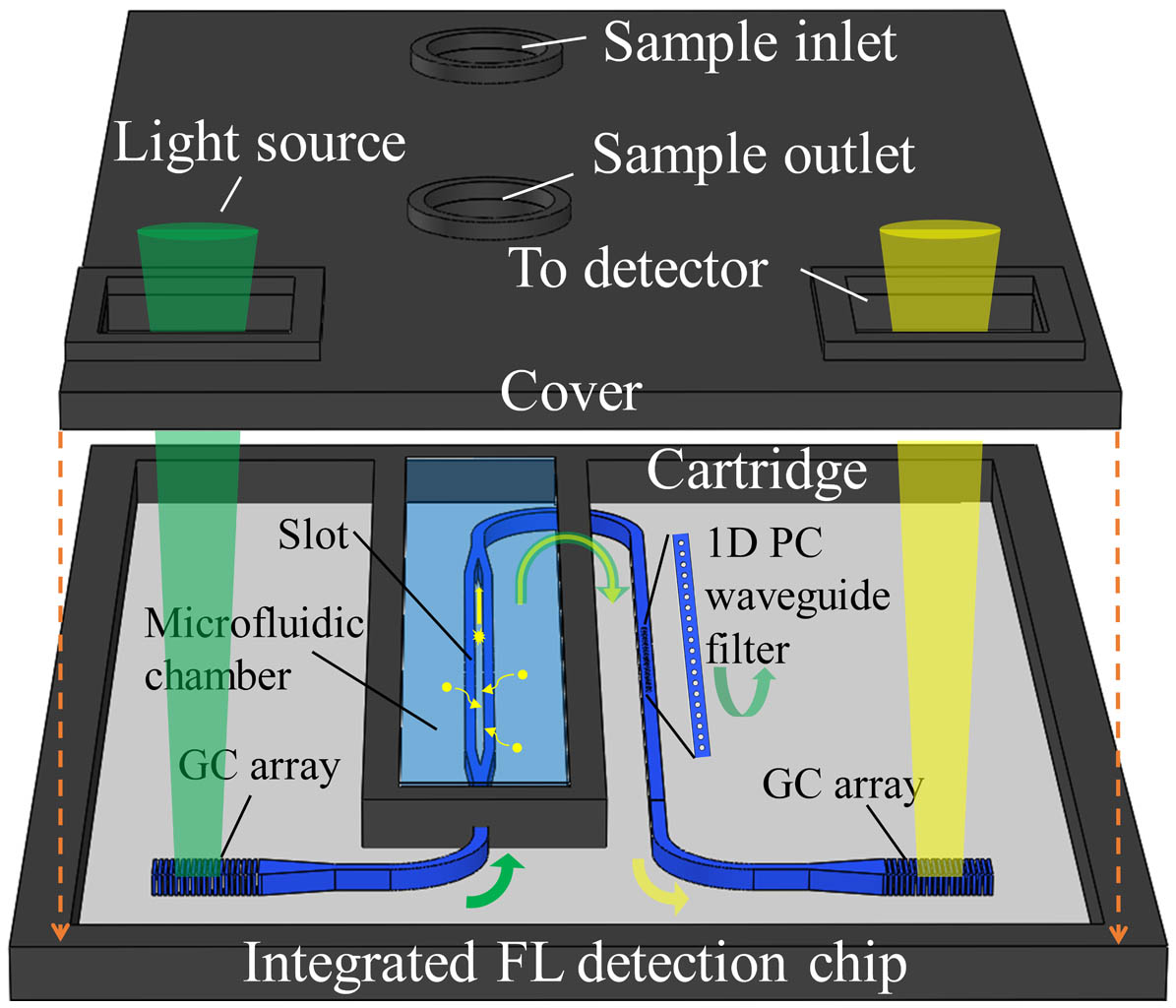
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 Key Laboratory of Intelligent Optical Sensing and Integration of the Ministry of Education, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210009, China
3 College of Science, Wuxi University, Wuxi 214411, China
Fluorescence detection is widely used in biology and medicine, while the realization of on-chip fluorescence detection is vital for the portable and point-of-care test (POCT) application. In this Letter, we propose an efficient fluorescence excitation and collection system using an integrated GaN chip consisting of a slot waveguide and a one-dimensional photonic crystal (1D PC) waveguide. The slot waveguide is used to confine the excitation light for intense light–sample interaction, and the one-trip collection efficiency at the end of slot waveguide is up to 14.65%. More interestingly, due to the introduction of the 1D PC waveguide, the fluorescence signal is directly filtered out, and the excitation light is reflected to the slot waveguide for multiple excitations. Its transmittances for the designed exciting wavelength of 520 nm and the fluorescent wavelength of 612 nm are 0.2% and 85.4%, respectively. Finally, based on numerical analysis, the total fluorescence collection efficiency in our system amounts to 15.93%. It is the first time, to our knowledge, that the concept of an all-in-one-chip fluorescence detection system has been proposed, which paves the way for on-chip fluorescence excitation and collection, and may find potential applications of miniaturized and portable devices for biomedical fluorescence detection.
fluorescence slot waveguide photonic crystal on-chip Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 101203
1 南京大学 集成电路学院,苏州 215163
2 南京大学 电子科学与工程学院,南京 210093
3 西北大学 化学与材料科学学院,西安 710069
4 四川大学 物理学院,成都 610065
5 中山大学 微电子科学与技术学院,珠海 519082
6 西安交通大学 电子科学与工程学院,西安 710049
7 南京大学 现代工程与应用科学学院,南京 210093
人工设计的光子学器件在现代光学的各个领域都有广阔的应用前景。传统光子学器件的设计通常是基于已知的物理模型,然后通过数值模拟方法对结构进行优化设计。由于器件结构很大程度上依赖于先验模型,所以传统优化设计的自由度是有限的。随着近年来对高性能光子学器件需求的日益增长,具有更高设计自由度的逆向设计方法得到了快速发展。逆向设计方法打破了传统方法的设计局限性,可以在全参数空间中实现高效的参数优化,因此更可能得到具有极限性能的器件结构。本文总结了光子学器件逆向设计的常用方法,并给出了逆向设计在各个光子学领域中的具体应用。随着计算机科学的不断发展,逆向设计方法展现出无与伦比的潜力,有望在各个光学领域中实现更高自由度的光场调控。
遗传算法 梯度下降算法 拓扑优化 神经网络 纳米光子学 Genetic algorithm Gradient descent algorithm Topology optimization Neural network Nanophotonics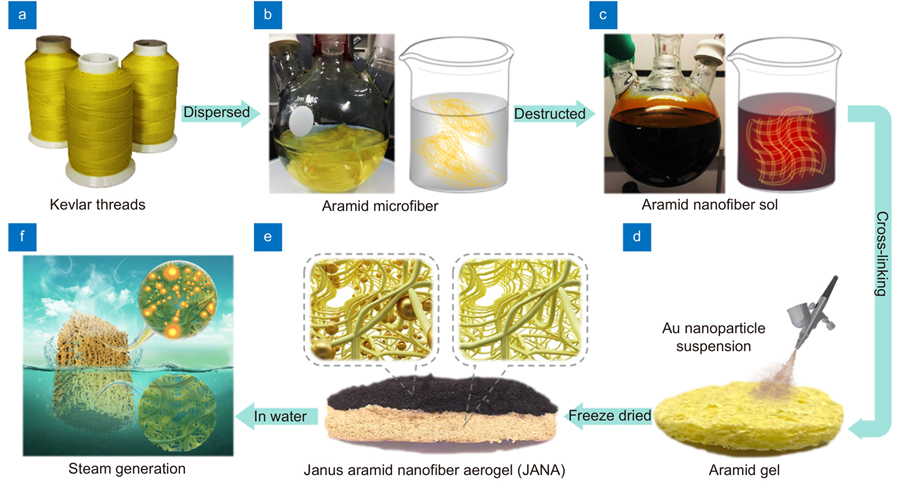 
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid-State Microstructures, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing 210093, China
Interfacial solar steam generation (ISSG) is a novel and potential solution to global freshwater crisis. Here, based on a facile sol-gel fabrication process, we demonstrate a highly scalable Janus aramid nanofiber aerogel (JANA) as a high-efficiency ISSG device. JANA performs near-perfect broadband optical absorption, rapid photothermal conversion and effective water transportation. Owning to these features, efficient desalination of salty water and purification of municipal sewage are successfully demonstrated using JANA. In addition, benefiting from the mechanical property and chemical stability of constituent aramid nanofibers, JANA not only possesses outstanding flexibility and fire-resistance properties, but its solar steaming efficiency is also free from the influences of elastic deformations and fire treatments. We envision JANA provides a promising platform for mass-production of high-efficiency ISSG devices with supplementary capabilities of convenient transportation and long-term storage, which could further promote the realistic applications of ISSG technology.
plasmonics interfacial solar steam generation broadband optical absorption aerogel Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(5): 220061





